Cloud computing is evolving with every passing day, and innovations in cloud computing are a new norm these days. We will be comparing two of the popular cloud computing technologies, Container as a Service (CaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) through this blog.
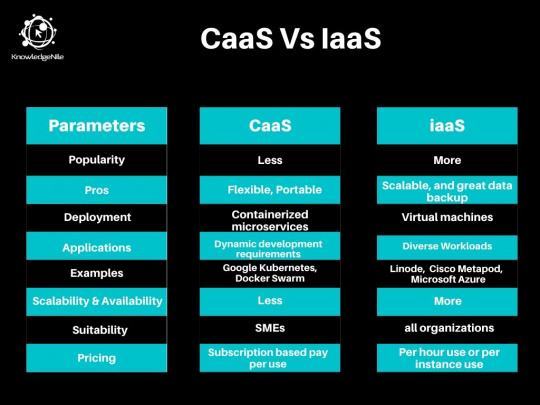
This comparison includes parameters like popularity, deployment methods, applications, examples, scalability, and suitability, etc. Most often, CaaS is considered as a subset of IaaS, but its functionalities differ from that of CaaS.
CaaS vs. IaaS: Top 8 Differentiating Factors
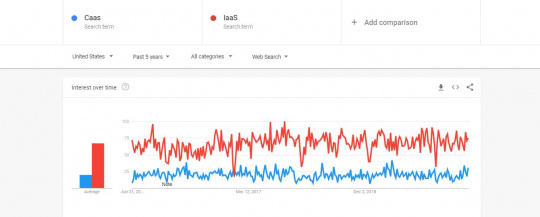
We can see from the above-mentioned graph that IaaS is more popular than CaaS over the last five years though there have been some periods of time when both the cloud computing technologies were at par in terms of popularity.
Container as a Service (CaaS) is a cloud computing platform that allows the organizations to deploy full-fledged microservices locally.
This functionality helps the companies to reduce the time required for development cycles.
On the other hand, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a platform that allows the companies the basic infrastructure like attachable storage, virtual machines (VMs), and software-defined networking (SDNs).
CaaS is more useful when your IT team needs to have more control over application components as you can easily deploy complex operations on containers.
Hence, whenever you have flexible requirements and need to manage or change the components, CaaS is your ideal go-to option.
While IaaS is more useful when you have to work on customer-centric web applications, operations like SAP, and where you need to ease the on-premise workload. In simpler words, IaaS is more useful with workload diversity, data warehousing, development and testing environments.
The key examples of CaaS include Google Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, Rackspace Carina, Apache Mesos, etc.
On the other hand, the key examples of IaaS include Linode, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metapod, Google Compute Engine, and Microsoft Azure, etc.
Container as a Service have higher flexibility, but they are not as easily scalable as most of the cloud computing platforms. But, a being container platform, it tends to have higher availability.
On the other hand, Infrastructure as a Service offers better scalability than CaaS does. Its availability is much higher, but it is less than that of CaaS.
Also Read: PaaS vs. SaaS: Detailed Difference Between the Two
CaaS is more suitable for service industry companies whose development requirements are often changing and are dynamic in nature. Typically, CaaS is more suited to small to medium size businesses.
On the other hand, IaaS is more suited to virtualization requirements with flexible workloads. Typically, IaaS is also more suited to small to medium size businesses.
The key difference between CaaS and IaaS in terms of suitability is CaaS is more suitable when development requirements are changing, and IaaS is more suitable when the workloads are changing.
Pros of CaaS:
- Greater flexibility in development requirements.
- Ease of deploying complex and multi-layered applications.
- Ease of integration with other applications through APIs.
- Greater portability.
Cons of CaaS
- Higher lock-in periods.
- If there are server issues at provider's end, your system will also have a downtime.
- Higher costs.
- Even though it is easier to deploy the apps, still you require a skilled workforce to develop containerized applications.
Pros of IaaS:
- Virtualization of hardware gives you more scalability.
- Ease of sharing the workload.
- Ease of data storage and data backup.
- Pay as you use.
Cons of IaaS
- Performance issues could be a factor in some cases.
- Availability issues.
- Difficulty in migrating the data if you change the service provider.
- Though operational costs are reduced, overheads are increased due to virtual machines.
Typically CaaS providers offer a free trial and mostly based on public cloud platforms. The pricing models are subscription-based and are billed as per the usage monthly, mostly with some deployment fees upfront.
Most of the IaaS providers also offer a free trial. The pricing models are based on the utility of virtual machines. They are priced at per hour usage or per-instance uses based on the service providers' offerings.
Caas Vs. IaaS: Key Takeaways
In this digitally transformed world, companies are going for the multi-cloud approach and not relying on only one service platform.
You can use either of these solutions or even both of them as per your requirements. You can use CaaS for the application development process wherein there is a need for flexibility, and you can go for IaaS when the virtual workloads are varying.
Also Read: CaaS vs. PaaS: Understand the Difference Between two Cloud Computing Services