Today organizations are using Edge, Cloud, And Fog Computing services to manage their data and applications. Edge, Cloud, And Fog Computing may have some standard features but are different layers of IIoT. These technologies allow the organization to take advantage of data storage resources. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a growing industry that requires more efficient ways to manage data transmission and processing.
Edge Computing in IoT
These devices are physical devices that are located in a remote location. These devices also have a sufficient amount of memory and computing resources used to collect and process the data.
IoT devices are the source of data that is connected to the internet. an edge device collects and processes the data. Edge computing device stays closer to the source of data, such as IoT devices. IoT produces a large amount of data. This data is to be processed and analyzed so it can be used. As edge computing moves the computing services like storage and servers closer to end-user or source of data, data processing becomes much faster with lower latency and also saves bandwidth.
Without Edge computing, the data from IoT devices have to be sent back and forth to the cloud, resulting in slower response time and less efficiency.
Benefits of Edge Computing
The benefits of edge computing are as follows:
- Edge computing reduces network cost and transmission delay to provide better control over sensitive data movements.
- Augmented reality and virtual reality applications also benefit from lower response times.
- It enhances security since the data does not travel over a network. Data is distributed so the local data might remain safe if the data center gets compromised.
- It is challenging to transfer all the data to the cloud at once. Also, when you don’t have an internet connection, you cannot access the cloud.
- Edge computing stores data locally and only send some of the data to the cloud. It can also wait to send data till the bandwidth is available.
Fog Computing in IoT
Fog Computing which is also known as fog networking or fogging, is a decentralized computing structure located between devices that produce data like IoT devices and the cloud. The main goal is to provide basic analytic services at the edge of the network. This also improves performance and overall network efficiency due to less distance across the network. The devices which extend the cloud closer to the source of data are called fog nodes.
Features of Fog Computing
- Enhance security
- Boost business agility
- Improve reliability
- Minimize latency
Fog computing analyses the data at the network edge, which is time-sensitive instead of sending the IoT data to the cloud. moreover, it takes just milliseconds to act on the data.
Cloud Computing
It is the distribution of on-demand computing services. This also includes servers, storage, databases, software, networking over the internet. Cloud computing also offers you flexible resources and faster innovation. This also helps to lower your operating costs as you will be paying only for the cloud services you use.
Many software vendors are also using cloud computing as a default option for their applications. Moreover, rather than owning a data center or a computing infrastructure, companies can also rent cloud service providers for applications and storage purposes.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a major shift from traditional on-premises IT. The following are the common reasons why companies and organizations are moving towards cloud computing services.
Cost
Cloud computing eliminates most of the cost and efforts of purchasing the datacenters, hardware and software, the electricity need to power and cooling of the data centers and hardware, the installation and the maintenance of the infrastructure.
Speed
Instead of waiting for months and week to purchase and configure the hardware, cloud computing services provide large amount of computing resources within minutes.
Global Scale
Cloud computing services deliver the right number of resources. Organizations can scale the capacity as per their needs. This avoids purchasing excess capacity.
Productivity
As discussed, cloud computing removes many hardware and datacenters that require IT experts to manage the infrastructure, so now the IT teams can spend their valuable time on business productivity.
Types of Cloud Computing
Based on the data and application, there are three types of cloud computing.
Public Cloud
Public clouds services are elastic and readily scalable. Third-party cloud service provider owns and manages public clouds which delivers computing resources over the internet.
Private Cloud
A single business or organization which exclusively uses computing resources refers to private cloud. A private network maintains the services.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is a combination of private and public cloud. A hybrid cloud gives more flexibility by allowing data and application sharability between private and public cloud.
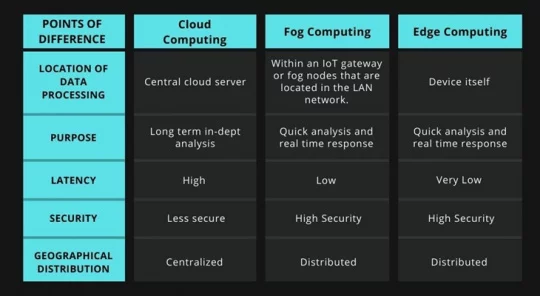
Edge & Cloud & Fog Computing Key Differences
Is edge computing better than cloud computing?
Edge computing and cloud computing are different technologies and it is also non-interchangeable. Time-sensitive data is processed on edge computing, whereas cloud computing is used for data that is not time-driven. It can’t replace cloud computing data because cloud computing is a centralized process that is the need for some time.
Conclusion
Cloud, Fog, and Edge computing technologies have irreplaceable solutions to many IoT challenges. The IoT has increased the needs of these technologies. Companies know how to implement cloud, fog, and edge technologies to support their needs. Workload should be categorized into monitoring, analyzing, and execution.