All enterprises, big or small, are in the race towards automation. Every organization wants to inculcate it in their business processes.
Within automation, there are various forms of it. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Cognitive Automation are two popular forms of automation.
It doesn’t take much for enterprises to mistakenly choose the wrong one. If you are struggling to understand the difference between the two, fret not. We will find out here, what is the difference between RPA and Cognitive Automation.
RPA vs. Cognitive Automation: A Quick Comparison
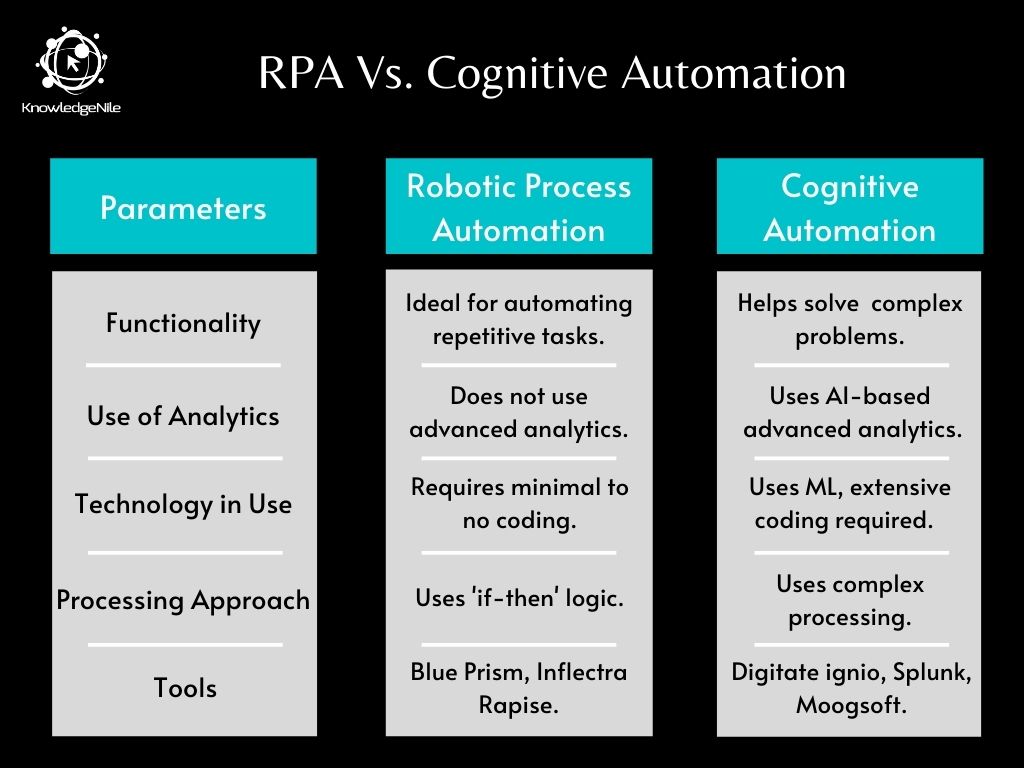
RPA involves automating menial and repetitive tasks. Cognitive automation includes adding the extra layer of AI and ML to it.
It mimics human-like decision making and functioning capability. This helps solve more complex problems and receive key insights from complex data as well.
RPA does not involve advanced analytics. It mostly delves into statistics of the tasks performed. It maintains an audit of the achievements and performs basic analytics on it. It works with a minimal set of commands.
Cognitive automation performs complex analytics on the data.
Tasks such as finding out the root cause of an issue, autonomously resolving the issue, or learning ways to fix, cognitive automation can do all that.
The added layer of AI and ML on it enables new capabilities over RPA. Self-heal, quick triaging are some capabilities of Cognitive Automation.
RPA mostly includes configuring and deployment of certain frameworks for it to function. It does not require coding. It’d be minimalistic if at all needed.
Some technologies that it uses include workflow automation, screen scraping, and macro scripts, among others.
Cognitive automation requires a lot of coding since it uses Machine Learning for its efficient functioning.
It uses advanced technologies such as data mining, natural language processing, semantic technology, text analytics, and so on.
Also Read: 10 Best Practices for RPA Change Management
One of the significant differences between RPA and cognitive automation is the way it processes data.
Since there is no coding involved in RPA, it uses a simple ‘if-then’ logic to function most of the time.
It is not capable of handling a varied level of exceptions. In case it comes across any, it merely transfers the problem to the human resolution queue.
This brings a certain level of dependency to its functioning and capabilities.
Cognitive automation is capable of mimicking human behavior and thinking.
With AI and ML capabilities, it can reason on the issues raised and tries to find the root cause and resolves it from the core.
In the case of unique exceptions, Cognitive Automation does transfer the issue to the human queue.
But it also learns from the human resolution technique. Hence, if such an issue resurfaces, cognitive automation knows how to resolve it.
This adds new capabilities to it with time, and hence it is more capable of resolving complex issues and a wide array of exceptions.
Some of the top RPA tools available in the market are:
- Blue Prism
- Inflectra Rapise
- UiPath
- IBM Automation Anywhere
Cognitive Automation tools in the market include:
- Digitate ignio
- Splunk
- Moogsoft
- Automation Edge
Conclusion
As we see from the points above, both RPA and Cognitive Automation are from two different ends of the same automation spectrum.
Even though they share some similar underpinnings, they have distinct differences.
At the end of the day, it drills down to what kind of functions enterprises aim to automate. Based on this, they can opt for a particular automation form, which suits them the best.
You May Also Like to Read:
5 Use Cases of RPA in Financial Services